What is DKIM? How to set it?
- What is DKIM?
- Why do you need a DKIM signature
- How DKIM Works
- How to set up a DKIM signature
- DKIM Signature Verification
- Benefits of DKIM
- Common issues with DKIM
- Key points
What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is considered to be a method to verify that the content of the messages is trustworthy, meaning that it hasn't changed from the moment the message left the initial mail server. This additional layer of trustability is achieved by an implementation of the standard public/private key signing process. Once again the owners of the domain add a DNS entry with the public DKIM key which will be used by receivers to verify that the message DKIM signature is correct, while on the sender side, the server will sign the entitled mail messages with the corresponding private key.
Suppose Chuck wants to trick Alice, who works for example.com, into sending him confidential company information. He could send her an email that seems to be coming from "bob@example.com" to fool her into thinking he also works for example.com.
DKIM, along with Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC), makes it much more difficult for attackers to impersonate domains in this way. Emails that do not pass DKIM and SPF get marked as "spam" or are not delivered by email servers. If example.com has DKIM, SPF, and DMARC set up for their domain, then Alice will probably never even see Chuck's malicious email because it will either go to her spam folder or be rejected by the email server altogether.
A DKIM signature is a TXT record that is added to the site's DNS zone settings. The entry itself looks like this:
us._domainkey TXT v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX,
where v — DKIM version, always takes the value v=DKIM1;
k — key type, always k=rsa;
p — This field contains the public key used to verify the DKIM signature. The public key is a base64-encoded string that corresponds to the private key used to sign the email which can be generated in the mailing service.
Please follow these guides in order to setup a DKIM record for Google Workspace and Microsoft 365.
Why do you need a DKIM signature
- Protects from scammers
A DKIM signature will prevent spammers from sending emails on your behalf. Together with SPF and DMARC, this technology will protect your subscribers from fraudsters, including identity theft.
- Increases deliverability
DKIM improves domain reputation. Using DKIM, the receiving server determines the authenticity of the sender and its overall rating. Emails with a good reputation are more likely to end up in the inbox.
DKIM works like an ID: you present it to the mail provider, and he lets you into the inbox. - Gives access to postmasters
Postmasters are mail services for mailing analytics. They help track deliverability, opens, unsubscribes, and spam complaints. To enable statistics in the postmaster, you must have email authentication configured. DKIM is one of the components of email authentication.
How DKIM Works
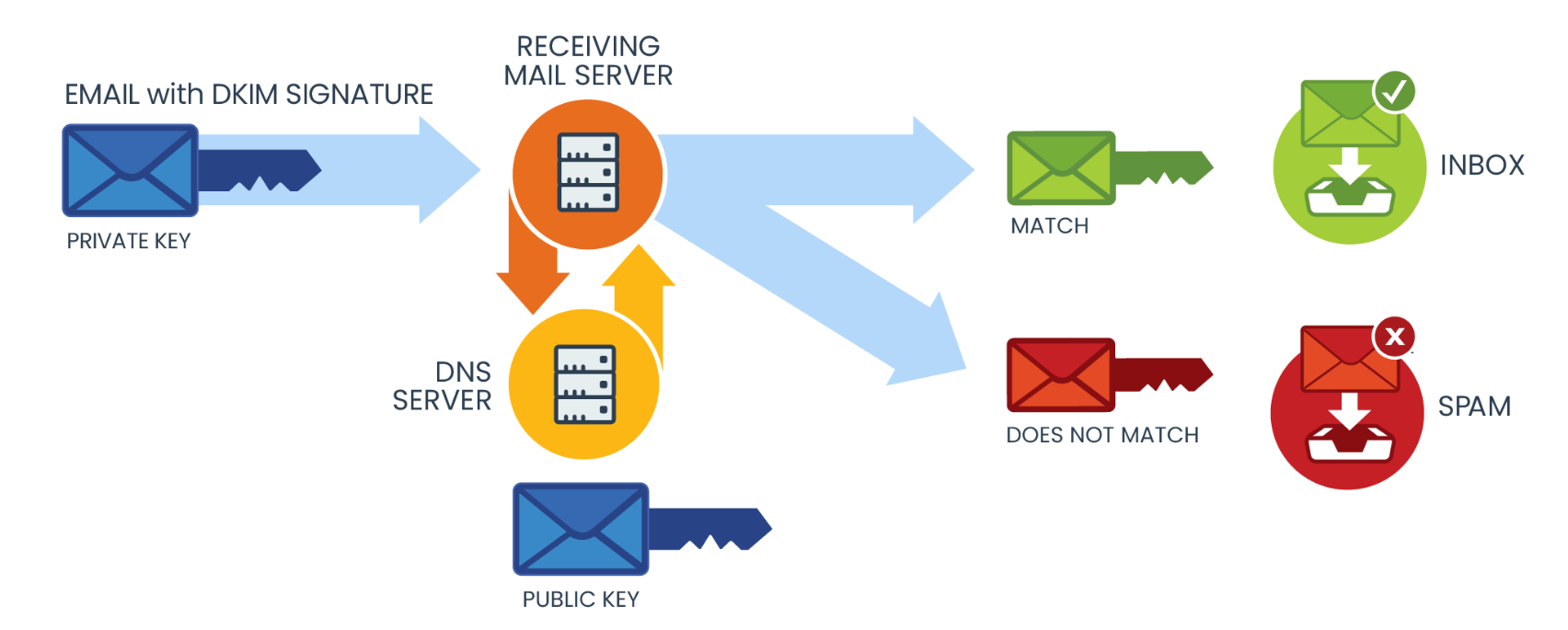
DKIM works like this: you are sending an email message using test@example.com. Before sending a message, the sending mail server will generate a DKIM signature header using a private key.
The mail system will start the DKIM verification by ensuring the DKIM signature matches the sender’s information.
When the message is delivered, the receiving email server will obtain the DKIM record from example.com’s DNS record. The receiving email server then uses the public key in the DNS record to verify the message’s DKIM signature.
If the public DKIM key matches the information in the signature, the message is proven to be authentic and will be moved to the inbox. This means that no one has altered the message in transit.
If the DKIM key doesn’t match the information, the message will most likely go to the spam or junk folder.
How to set up a DKIM signature
Setting up DKIM involves accessing the site's DNS zone and corporate email. Typically, SPF and DKIM records are generated in the email service provider's dashboard and added through the hosting provider's account.
-
Generate DKIM Records: Create a DKIM record within your email service provider's settings.
-
Add to DNS Settings: Insert the generated DKIM record into your domain's DNS settings. The record includes essential details such as the DKIM version, key type, and a unique code.
DKIM Signature Verification
After setting up a DKIM signature, it's worth checking if it works correctly. This can be done using our service, if your mailbox is connected to Warmy using "Check DNS records" test, or using third-party services, such as Mailtester.
MailTester.com - a service with which you can test a letter, including verifying the DKIM signature. MailTester gives you a complete deliverability report and also checks your email authentication settings.
You will be prompted to send a test email to the provided email address, after which you will be able to receive a detailed report about your mailbox.
All this will be evaluated on a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 - you are most likely to land in the SPAM folder, and 10 - you will definitely get into your recipient's Inbox.
Benefits of DKIM:
-
Email Authentication:
- Prevents Spoofing: DKIM helps ensure that the sender's domain is legitimate, making it harder for attackers to impersonate a sender.
- Enhances Trust: Recipients can trust that emails are from verified sources, leading to better engagement and communication.
-
Email Integrity:
- Content Protection: By signing emails, DKIM ensures that the content has not been tampered with during transmission. If the content is altered, the signature will not match upon verification.
-
Improved Deliverability:
- Reduced Spam Flagging: Emails with valid DKIM signatures are less likely to be marked as spam or junk by recipient mail servers, improving overall email deliverability rates.
- Enhanced Sender Reputation: A strong DKIM implementation can contribute positively to your domain's sender reputation, helping you avoid blacklisting.
-
Supports Other Authentication Protocols:
- Works with SPF and DMARC: DKIM can be used in conjunction with SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) for a layered security approach, providing comprehensive protection against email fraud.
-
Audit Trail:
- Email Tracking: DKIM provides an authentication mechanism that can be used for auditing and tracking email messages, helping organizations maintain a record of communications.
-
Business Credibility:
- Professional Image: Using DKIM can enhance a business's reputation, showing that it takes security and authentication seriously.
- Professional Image: Using DKIM can enhance a business's reputation, showing that it takes security and authentication seriously.
Common Issues with DKIM
-
DNS Propagation Delays:
- Time Lag: Changes made to DNS records can take time to propagate (up to 48 hours), which may cause temporary verification failures after setting up DKIM.
-
Configuration Errors:
- Syntax Mistakes: Incorrect formatting in the DKIM DNS record can lead to failure in validation. Common errors include typos, incorrect selector names, or missing fields.
- Key Management: Failing to properly manage the public/private key pair can result in mismatches during the verification process.
-
Key Length and Security:
- Insufficient Key Length: Using short keys (e.g., less than 1024 bits) can compromise security. It is recommended to use at least 2048-bit keys for strong encryption.
- Key Rotation: Regularly updating keys without proper planning can lead to downtime if new keys are not correctly published and configured.
-
Email Client Compatibility:
- Limited Support: Not all email clients display DKIM signatures or offer verification, which can lead to misunderstandings about the email’s authenticity.
-
Email Forwarding Issues:
- Forwarding Challenges: When emails are forwarded, the original DKIM signature may not be valid anymore, as the content can change. This can lead to legitimate emails being marked as fraudulent.
-
Lack of Reporting:
- No Feedback Mechanism: DKIM does not provide feedback to the sender regarding whether their emails were successfully authenticated or if there were any failures, unlike DMARC, which includes reporting features.
-
Spam Filters:
- False Positives: Even with a valid DKIM signature, certain spam filters might still flag emails based on other factors (like content or sender reputation), leading to unintended consequences.
Key points
Here is a table summarizing the key points of the article:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | DKIM is an email authentication protocol that helps protect your domain from phishing and enhance email deliverability. |
| Importance | DKIM helps to protect your domain from phishing and enhance email deliverability. |
| Function | DKIM works by adding a digital signature to emails. |
| Setup | To set up DKIM, you will need to create a DKIM record and add it to your domain's DNS settings. |
![Group 1261151152.png]](https://support.warmy.io/hs-fs/hubfs/Group%201261151152.png?width=50&height=50&name=Group%201261151152.png)